Proper maintenance of air compressors is vital to ensure operational reliability, energy efficiency, and a long service life, especially in industrial settings. Ignoring routine upkeep can lead to unexpected downtime, higher energy consumption, and costly repairs—disrupting production and straining budgets. This guide provides actionable maintenance strategies to help facility managers, engineers, and technicians optimize their compressed air systems and minimize risks.
1. Establishing a Preventive Maintenance Framework
| Maintenance Activity | Frequency | Key Actions | Tracking Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Checks | Daily | Inspect for leaks, wear, and cleanliness. | Manual Check / Digital Logs | Early identification of potential issues. |
| Performance Reviews | Weekly | Check performance parameters such as air pressure and flow. | Digital Logs / Performance Charts | Monitor trends to detect early problems. |
| Comprehensive Assessments | Monthly | Inspect all components: filters, oil, motor, etc. | Digital System / Physical Inspection | Complete overview of system health. |
| Filter Changes | As Needed (typically every 1-3 months depending on conditions) | Check and replace filters as required. | Digital Tracking / Maintenance Record | Frequency based on environment (dust, humidity). |
| Oil Analysis | Every 3-6 months or as recommended | Perform oil analysis for viscosity, acidity, and contamination. | Digital Tracking / Lab Reports | Adjust oil change frequency based on results. |
| Pressure Readings | Weekly or as per manufacturer recommendations | Measure air pressure across key points. | Digital System / Pressure Gauges | Monitor for abnormal drops. |
| Energy Consumption | Monthly | Measure specific power consumption (kW per m³ of compressed air). | Energy Monitoring System | Helps detect efficiency losses or issues. |
2. Critical Component Maintenance Procedures
2.1 Air Filter Management and Replacement
Intake filters play a key role in protecting compressors from contaminants. Regular inspection and timely replacement are essential to prevent pressure drops that can lead to increased energy consumption. Set a filter replacement schedule that suits your environment; facilities with high dust levels may require more frequent changes. Keep an eye on the differential pressure across filters, replacing them when the pressure drop exceeds manufacturer specifications—typically around 0.5 bar.
2.2 Oil and Lubrication System Maintenance
Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction, wear, and heat buildup in compressors. For oil-flooded compressors, it’s important to perform regular oil analyses to monitor key factors like viscosity, acidity, and contamination. Follow manufacturer guidelines for oil changes or adjust based on analysis results. For oil-free compressors, keep an eye on the sealing system and watch for any signs of lubricant contamination in the air stream.

3. Performance Monitoring and Efficiency Optimization
3.1 Pressure and Temperature Monitoring
Regularly monitoring operating pressures and temperatures is vital for early detection of potential problems. Install gauges at key points and establish baseline readings for normal operation. Keep track of discharge temperatures, cooler effectiveness, and motor temperatures. Abnormal readings often indicate issues with cooling, wear, or control faults that require immediate attention.
3.2 Energy Efficiency Verification
Routine maintenance directly impacts energy consumption. Periodically measure specific power consumption (kW per m³ of compressed air) and compare it to manufacturer specifications. Efficiency losses typically indicate leaks, pressure drops, or mechanical wear. An energy monitoring system can help identify trends, allowing you to prioritize high-impact maintenance actions to improve efficiency.
4. Troubleshooting Common Operational Issues
4.1 Identifying and Addressing Air Leaks
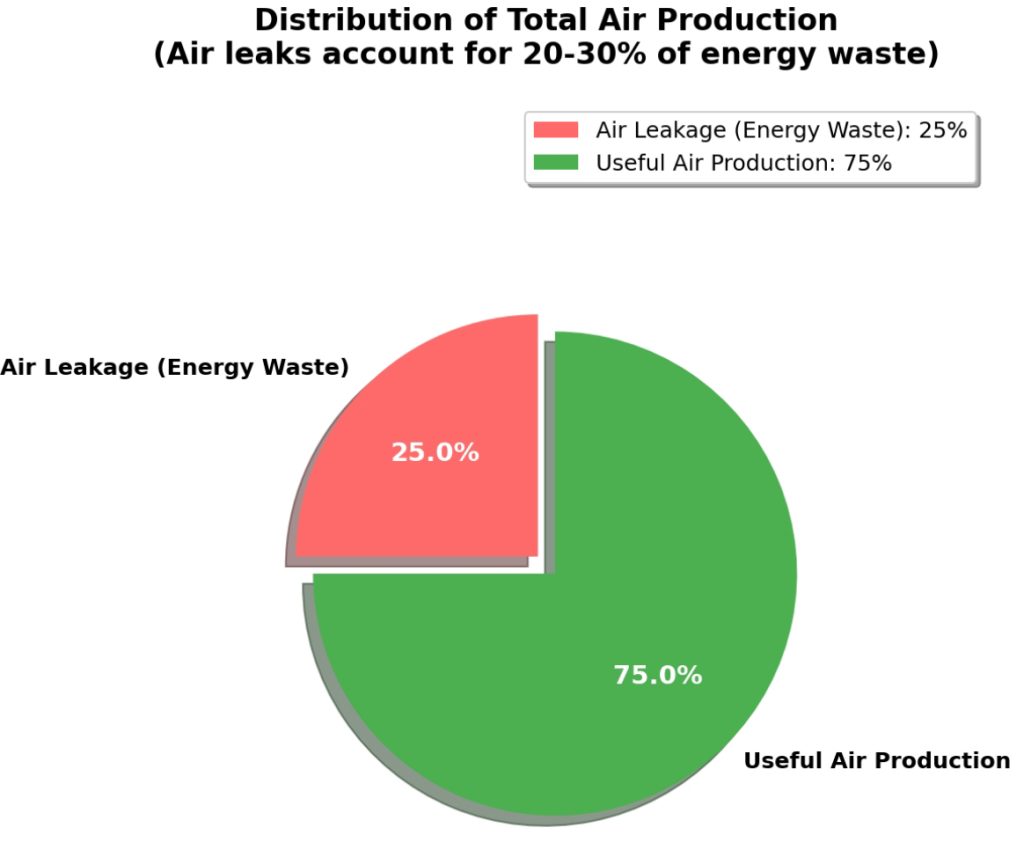
Air leaks are a significant source of energy waste, often accounting for 20-30% of total air production. Regular leak surveys using ultrasonic detectors can identify leaks during quiet production periods. Leaks should be tagged and prioritized for repair based on their size and complexity. Develop a leak repair program to address major leaks immediately, and schedule minor leaks for later maintenance cycles.
4.2 Vibration Analysis and Alignment Checks
Misalignment and excessive vibration can cause premature bearing wear and other serious mechanical issues. Incorporate regular vibration analysis into your maintenance strategy to detect problems early. Use laser alignment tools to ensure precise alignment of the motor and compressor, reducing vibration and extending the life of critical components. Schedule alignment checks during shutdowns or after replacing major components.
5. Safety Systems and Emergency Preparedness
5.1 Safety Valve and Relief Device Testing
Testing pressure relief devices regularly ensures their functionality during overpressure events. Implement a quarterly schedule for testing safety valves and rupture discs. Record set pressures and response times, replacing any devices that fail to meet specifications. Maintaining accurate records helps ensure compliance with safety regulations and ensures a safer working environment.
5.2 Electrical System Maintenance
Routine inspections of electrical components are crucial for preventing unplanned downtime. Check motor connections, contactors, and overload protection during scheduled maintenance windows. Thermographic imaging can help identify hot spots in electrical panels, signaling potential issues. Proper ventilation around electrical equipment is essential to prevent overheating and reduce the risk of failure.
Conclusion
A well-planned air compressor maintenance program is essential for maximizing equipment reliability, improving energy efficiency, and extending the service life of your machines. By adopting the strategies outlined in this guide, facility managers can create maintenance protocols tailored to their equipment and operational needs. Companies like Seize Air design their products with serviceability in mind, ensuring that their compressors perform optimally and remain energy-efficient throughout their service life.




 English
English
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português
 Deutsch
Deutsch






