As one of the most critical pieces of industrial equipment, air compressor failure can directly affect production efficiency and costs. With proper air compressor maintenance, technicians can quickly identify fault codes, minimize downtime, and keep operations stable.
This guide provides a detailed overview of the most frequent air compressor fault codes and their solutions, covering high temperature failure of air compressors, abnormal air compressor pressure, and air compressor electrical and mechanical failure. It also includes practical air compressor maintenance recommendations to help businesses optimize equipment management.
High Temperature Failure of Air Compressors
Temperature-related alarms are among the most common air compressor failures, often manifesting as excessively high or low exhaust temperatures. If not addressed promptly, they can reduce equipment lifespan and compromise safety.、

- E001 (High Temperature Alarm): Usually caused by insufficient coolant, blocked radiators, or faulty sensors.
- Solution: Check coolant flow, clean the radiator, confirm cooling fan operation, and ensure lubricant levels are sufficient.
- E004 (Excessive Supply Air Temperature): Linked to decreased heat exchanger efficiency, faulty sensors, or insufficient cooling medium.
- Solution: Clean or replace the heat exchanger, check sensor calibration, and confirm adequate cooling water/air flow.
- T1 Oil Temperature Too High: Caused by lubricant shortages, degraded oil, cooler inefficiency, or temperature control valve failure.
- Solution: Refill or replace lubricant, clean the cooler, and repair or replace faulty valves.
Quick Reference Table – Temperature Fault Codes
| Error Code | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|
| E001 | Insufficient cooling water, clogged radiator, sensor failure | Clean/repair cooling system, replace sensor |
| E004 | Heat exchanger malfunction, sensor error, insufficient cooling medium | Clean heat exchanger, check sensor, ensure cooling flow |
| T1 Too High | Low oil, degraded lubricant, cooler failure, valve malfunction | Refill/replace oil, clean cooler, repair valve |
| Low Exhaust Temp | Valve malfunction, excessive idle, faulty sensor | Repair valve, adjust operation, replace sensor |
Maintenance Note: For variable frequency compressors, always check VFD cooling fans, heat dissipation channels, and operating temperature to prevent overheating alarms.
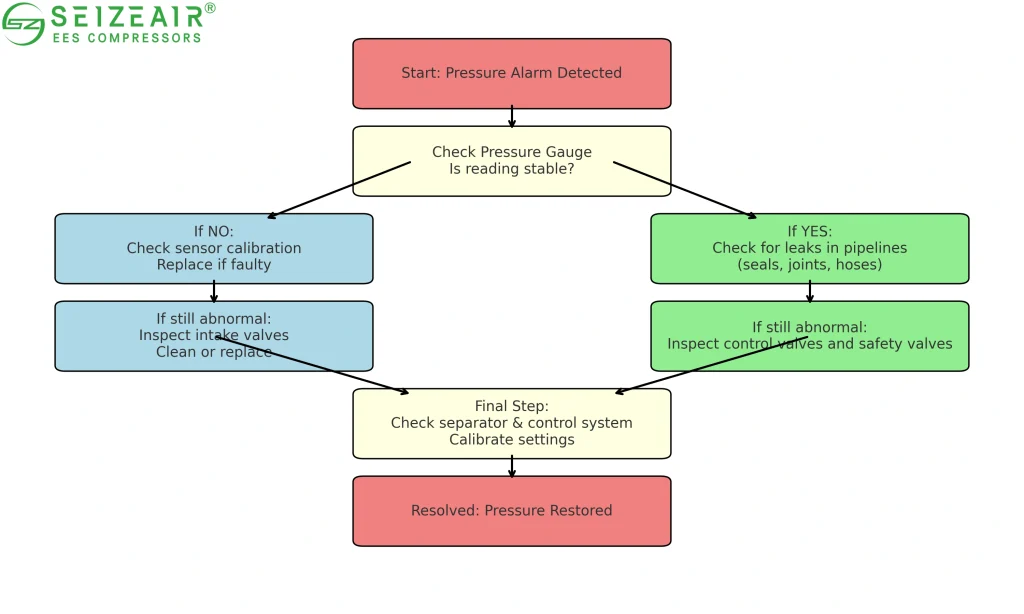
Abnormal Air Compressor Pressure Faults
Pressure system faults represent another major air compressor failure, leading to unstable gas supply or excessive energy consumption.
- E002 (Excessive Pressure): Caused by faulty regulating valves, safety valve failure, or pressure sensor malfunction.
Solution: Clean or replace valves, recalibrate safety valves, and confirm sensor accuracy. - E003 (Low Pressure): Often results from leaks, intake valve malfunctions, or sensor faults.
Solution: Inspect pipelines, test for leaks, clean intake valves, and calibrate sensors. - Safety Valve Activation: Indicates serious control failure, possibly from oil-gas separator blockage or safety valve fatigue.
Solution: Shut down immediately, replace fatigued valves, and check separator pressure drop (>0.8 bar).
Note for Variable Frequency Compressors: Check PID parameter settings, pressure sensor signals, and control logic to stabilize pressure regulation.
Air Compressor Electrical and Mechanical Failure
Electrical and mechanical faults often cause shutdowns and require urgent diagnosis.
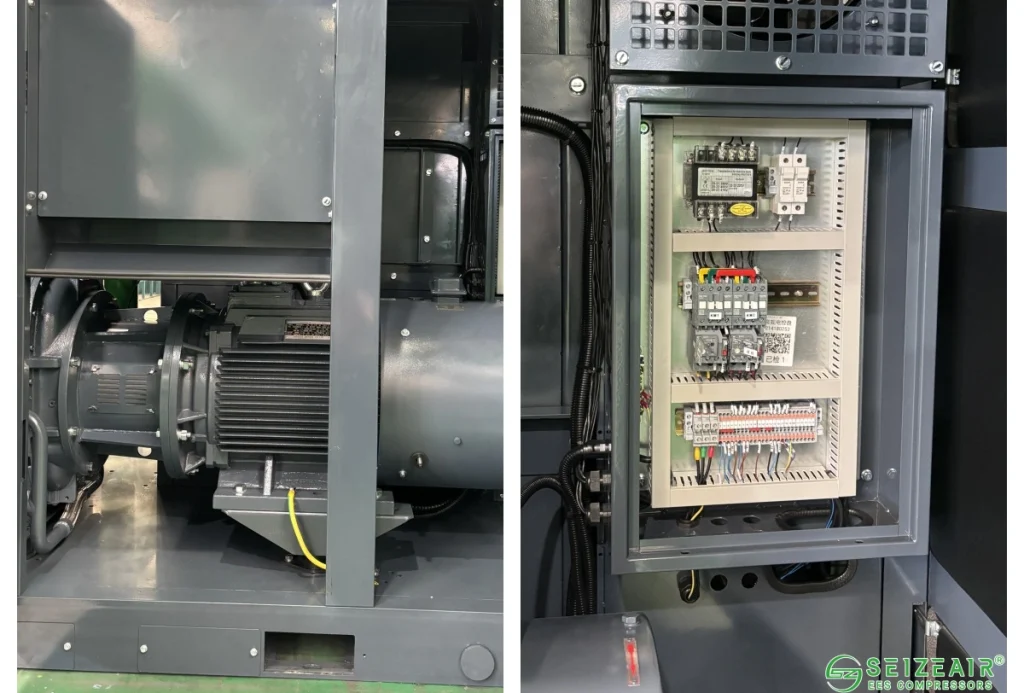

- E01 (Air Compressor Cannot Start): Possible causes include power issues, motor failure, or mechanical lockup.
Solution: Check power supply, test motor insulation, manually rotate the unit, and inspect relays/contactors. - OCF (Variable Frequency Drive Overcurrent Fault): Caused by motor overload, mechanical jams, or parameter mismatches.
Solution: Inspect transmission system, check motor windings, verify VFD settings, and inspect motor cables for hidden damage. - Main Unit Lockup: One of the most severe air compressor failures, often caused by poor lubrication or bearing wear.
Solution: Use manufacturer-recommended oil, replace filters regularly, and prevent foreign object ingress.
Mechanical Vibration Issues: Excessive vibration may indicate misalignment, worn couplings, or bearing clearance issues.
Solution: Perform precise alignment, inspect couplings, and balance rotating parts.
Other Common Faults and Solutions
Beyond temperature, pressure, and electrical issues, operators should also monitor:
- Excessive Oil Consumption: Often caused by return oil system failure, damaged separators, or excessive lubricant filling.
Solution: Clean oil lines, replace separators, and adjust oil level. - High Oil Content in Exhaust Air: Caused by faulty separators, return valve blockage, or unstable pressure.
Solution: Replace separator elements with OEM parts, clean valves, and stabilize system pressure. - Centrifugal Compressor Surge: A unique issue for centrifugal models, caused by low load or faulty guide vanes.
Solution: Inspect and calibrate guide vane actuators, optimize anti-surge parameters, and avoid surge ranges.
Air Compressor Maintenance Strategy
Preventive air compressor maintenance is the most effective way to reduce failures. Recommended service intervals:
| Maintenance Project | Content | Cycle |
|---|---|---|
| Lubrication System | Check oil, replace oil & filter | Every 2000 hours |
| Intake System | Clean/replace air filter | 2000–4000 hours |
| Oil-Gas Separation | Replace separator element | 4000 hours or ΔP > 0.8 bar |
| Cooling System | Clean cooler | Every 6 months |
| Safety Devices | Inspect safety valves & switches | Annually |
| Electrical System | Check wiring, contactors, sensors | Quarterly/Semi-annually |
Modern diagnostic systems allow remote monitoring and data analysis, helping technicians identify intermittent air compressor failures such as VFD overcurrent alarms or pressure fluctuations.
Safety Reminder: Always follow lockout/tagout procedures, depressurize systems before maintenance, and confirm smooth unit rotation before restarting.
Seize Air After-Sales Service Guarantee

While proper air compressor maintenance significantly reduces the risk of air compressor failure, Seize Air provides a comprehensive after-sales service system to give customers complete peace of mind. Our expert service team offers professional troubleshooting, genuine spare parts, preventive maintenance programs, and 24/7 technical support. From resolving high temperature failures of air compressors to correcting abnormal air compressor pressure or handling complex electrical and mechanical failures, Seize Air ensures your production never stops.





 English
English
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português
 Deutsch
Deutsch






