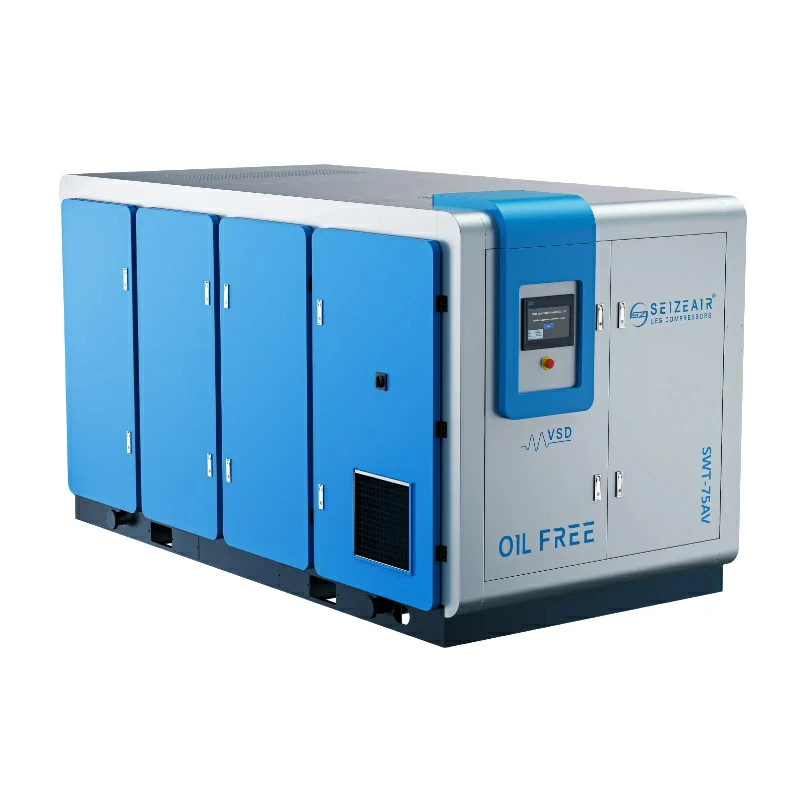
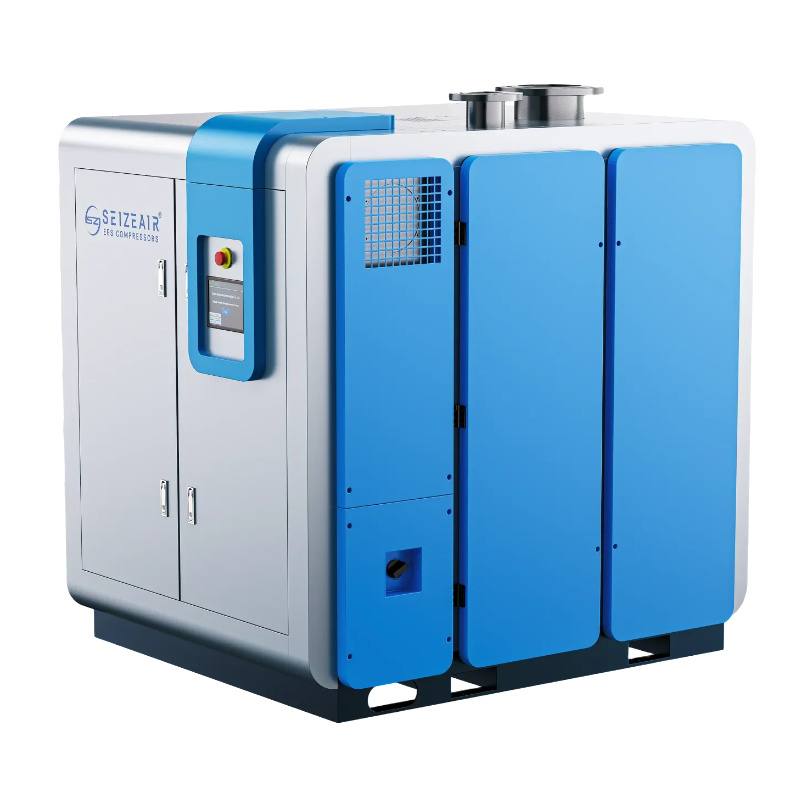
Introduction
Selecting the right compressed air system requires careful analysis. Large air compressors must match specific operational demands precisely. Understanding key technical parameters prevents costly mismatches. This guide outlines critical decision factors for industrial users.
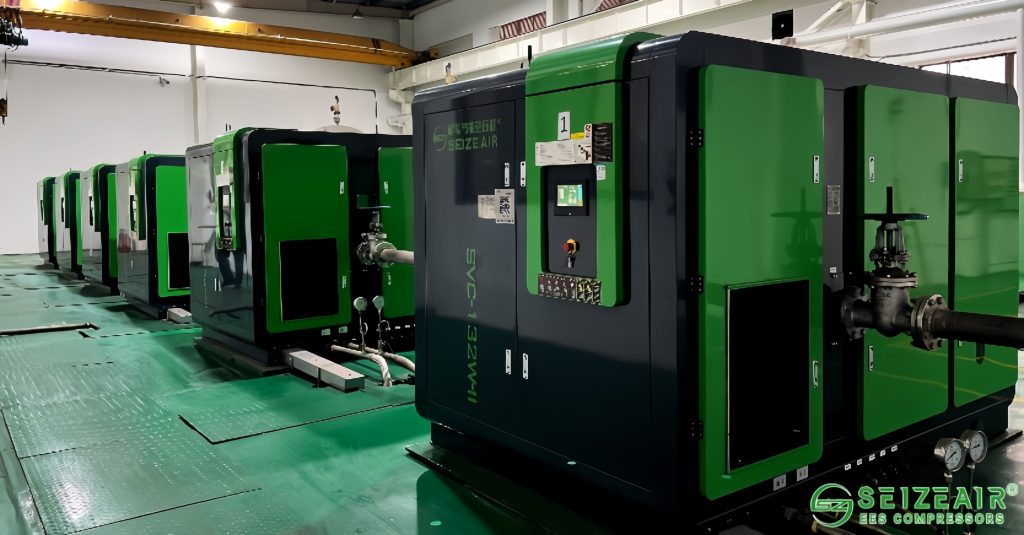

1. Determining Optimal Flow Rate Requirements
Flow rate remains the most fundamental selection parameter. Calculate total air consumption for all connected equipment. Include simultaneous usage factors and future expansion needs. Large air compressors should provide 20-30% capacity above peak demand. This buffer ensures stable pressure during production fluctuations. Undersized units cause pressure drops affecting tool performance.
2. Understanding Pressure Specifications
Different applications require specific pressure levels. Textile plants often need 0.3-0.5MPa for pneumatic looms. Laser cutting systems typically demand 0.8-1.25MPa for optimal operation. Consider pressure losses through filtration and piping systems. Energy efficient large air compressor models maintain pressure with minimal variance. Proper pressure matching reduces energy consumption significantly.
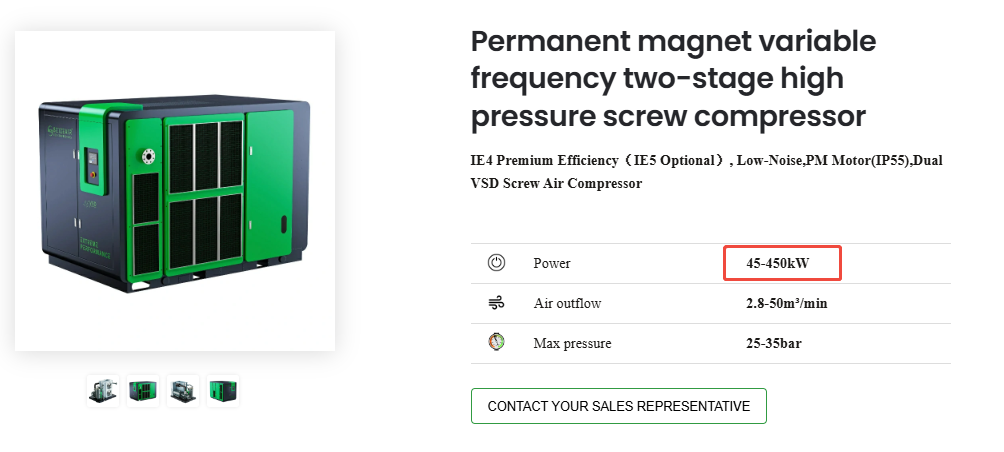
3. Evaluating Energy Efficiency Metrics
Energy costs typically represent 80% of total ownership expenses. Variable speed large air compressor models adapt to demand patterns intelligently. They can reduce energy consumption by 25-40% versus fixed-speed units. Compare specific power consumption (kWh/m³) across different models. Water cooled large air compressor systems often achieve better heat dissipation. This improves overall efficiency in high-ambient temperature environments.
4. Analyzing Duty Cycle Demands
Continuous versus intermittent operation affects compressor selection. Manufacturing facilities often require 100% duty cycle capability. Oil-free large air compressor models excel in continuous operation scenarios. They eliminate oil contamination risks in sensitive processes. Evaluate start-stop frequency and load cycling patterns. These factors impact component lifespan and maintenance schedules.
5. Environmental Considerations and Air Quality
Compressed air purity requirements vary by industry. Food and pharmaceutical sectors need Class 0 oil-free air certification. Water cooled systems reduce noise pollution in workplace environments. Consider heat recovery possibilities for facility heating. Proper ventilation extends equipment life and maintains performance.

6. Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
Look beyond initial purchase price to long-term operational costs. Maintenance requirements differ significantly between compressor types. Oil-free models eliminate oil changes and filter replacements. Variable speed drives reduce electrical demand charges. Calculate ROI based on energy savings and maintenance reductions.
Conclusion
Selecting industrial compressed air systems requires multidimensional analysis. Flow rate, pressure, and duty cycle parameters interrelate closely. Energy efficiency directly impacts operational profitability. Proper sizing ensures reliability while minimizing costs.
Companies like Seize Air specialize in engineering advanced compression solutions. Their oil-free screw compressors deliver reliable performance for demanding applications. Such manufacturers combine technical expertise with practical operational knowledge. They help industries optimize their compressed air systems effectively.




 English
English
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português
 Deutsch
Deutsch






