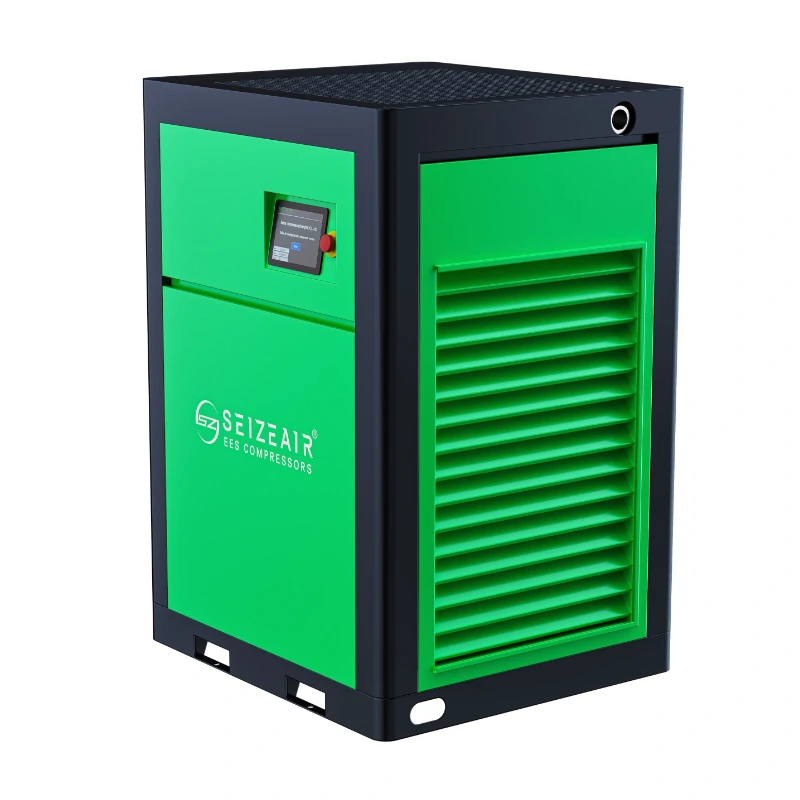
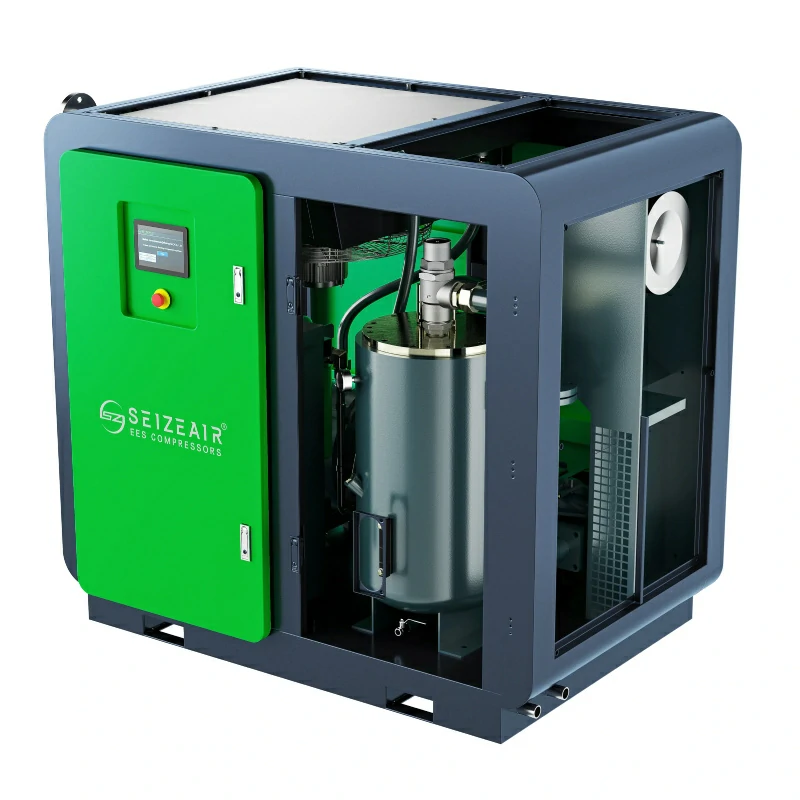
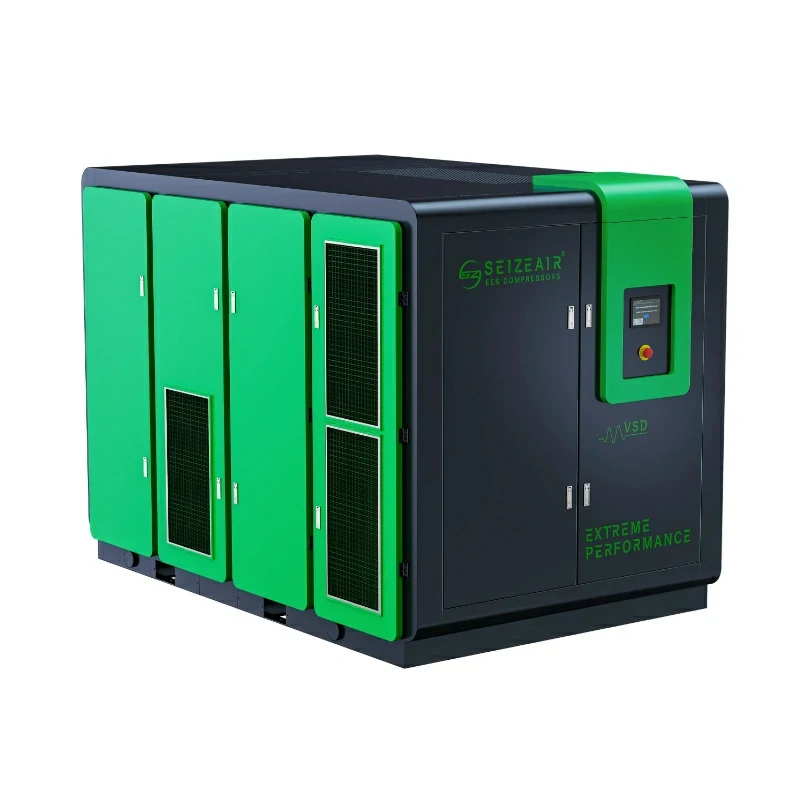
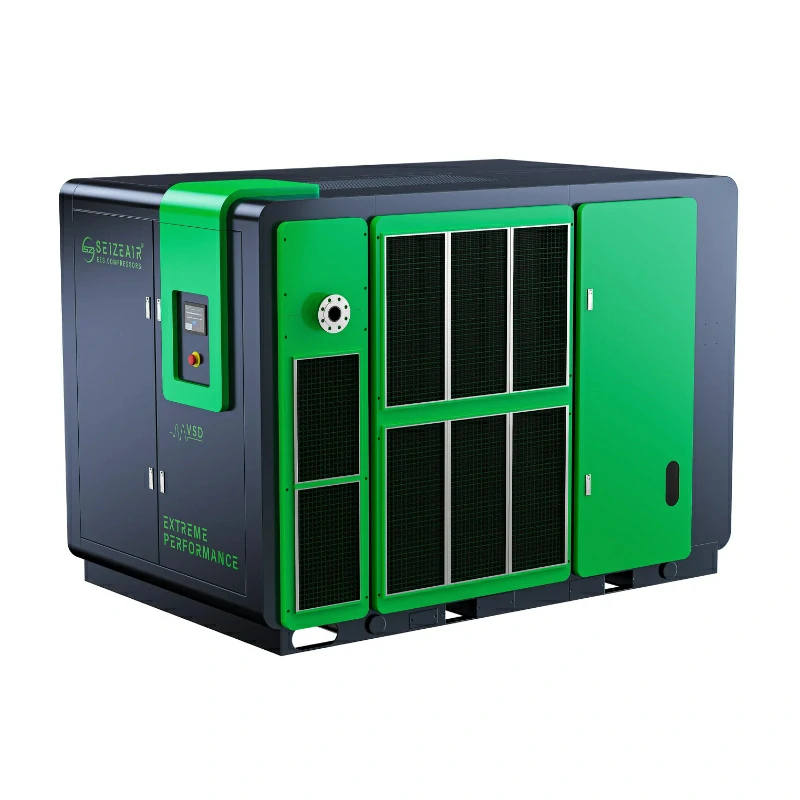
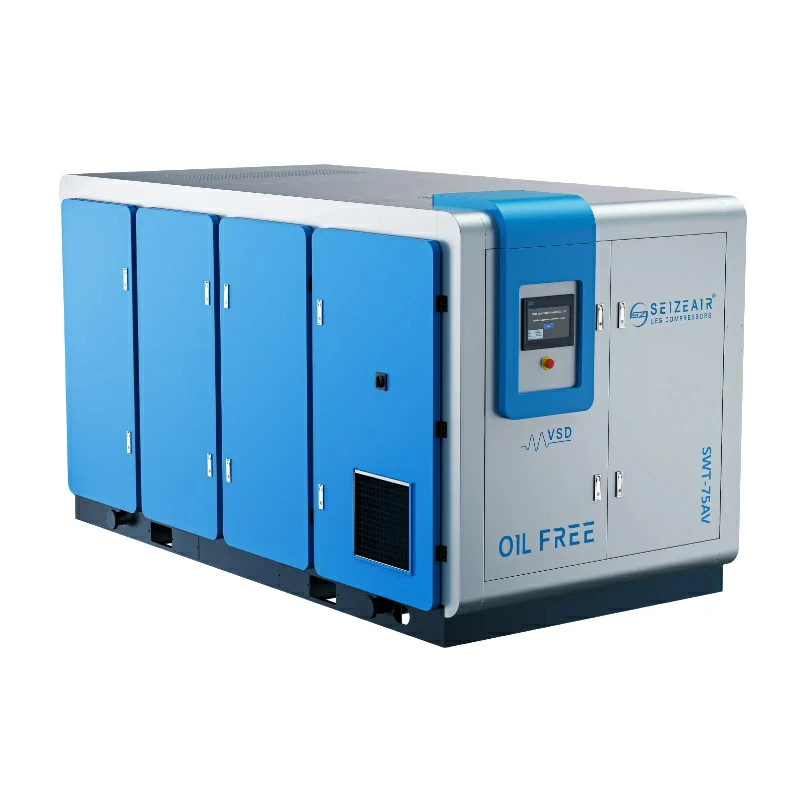
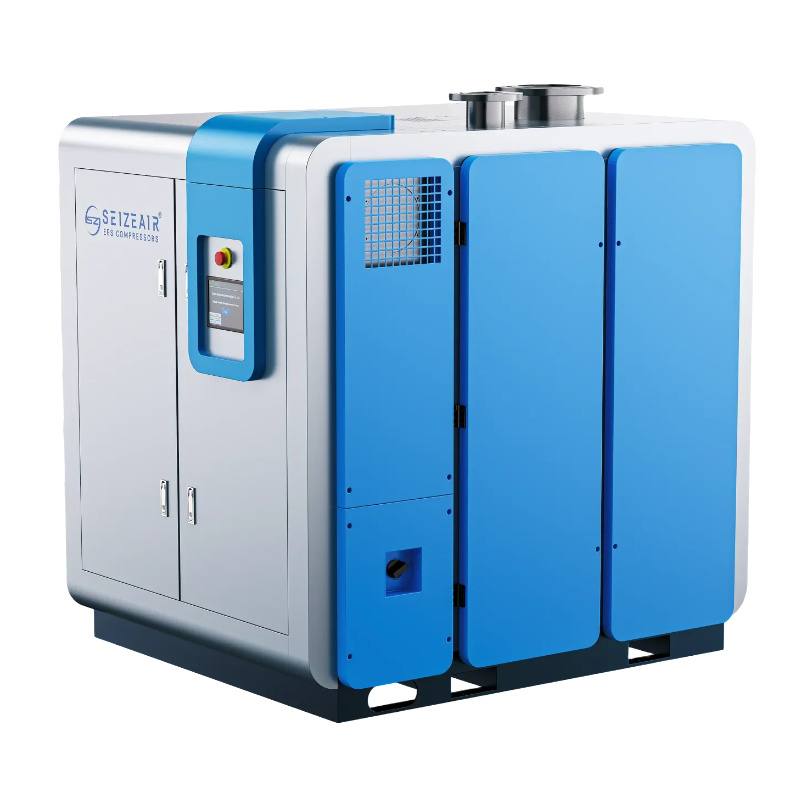
The industrial quiet air compressor marks a significant step forward in addressing noise pollution in the workplace while maintaining high performance. Factory managers and engineers are increasingly aware of the impact of excessive noise—not just on worker health and safety, but also on energy efficiency. Modern quiet compressors now operate at noise levels as low as 60-78 dB, similar to the sound of normal conversation, all while delivering the power needed for industrial operations.

1. Noise Reduction Technologies in Modern Compressors
SEIZE air compressors achieve low-noise operation through a variety of technologies, encompassing every aspect of the system, including air intake, compression, heat dissipation, and casing design:
1.1 Intake System Noise Reduction:
- Independent Intake Path: Completely isolates the air filter intake system from the main engine power compression unit, reducing noise at the source.
- S-shaped Intake Path and Noise Reduction Inclined Plates: Multiple noise reduction inclined plates are installed in the air intake duct, forming an S-shaped flow path. This reduces noise transmission without affecting flow rate, effectively reducing noise by 2-3dB.
- Non-through Design: Intake mesh holes are provided beneath the door panel, shielding the air filter intake from direct contact with the outside world, effectively reducing airflow noise.
1.2 Noise Reduction in the Casing and Internal Structure:
- Soundproofing: 30-50mm thick soundproofing is applied to key locations, such as the back of the intake door panel, inside the muffler housing, and on the back of the soundproof cover, achieving an overall noise reduction of 10-15dB.
- Sealing: Car-style sealing strips are applied to the folded edges of the door panels to enhance overall sealing and prevent noise leakage.
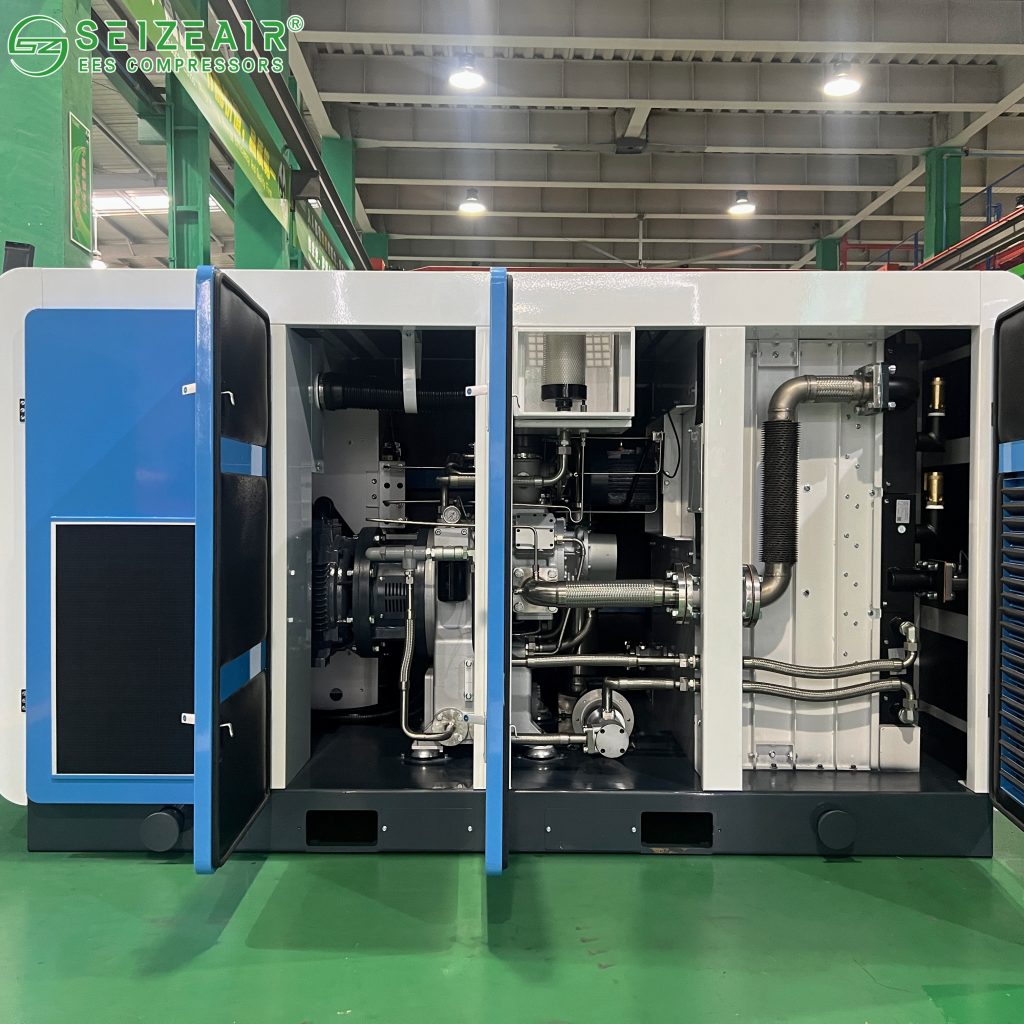

1.3 Noise Reduction in Core Components and Cooling System:
- Low-Speed Design: A design concept of large airend and low speed (e.g., a two-stage airend with a linear speed of 25m/s) is employed to fundamentally reduce mechanical noise.
- High-Efficiency Cooling Fan: Centrifugal fans from German brands (such as Rosenberg) are widely used. Compared to conventional axial-flow fans, centrifugal fans offer lower speeds, more uniform heat dissipation, and no air backflow, resulting in lower noise.
- Magnetic Levitation Bearing Technology (Magnetic Levitation Model): This achieves contactless and frictionless rotor operation, significantly reducing mechanical vibration and noise by 5-8dB.
1.4 Exhaust and Silencing System:
- Built-in Muffler: The unit features a built-in vent muffler, effectively reducing noise by 5-7dB when discharging compressed air.
- Customized Anti-noise Muffler: Used to reduce high-frequency noise generated by airflow.
2. Advantages of Low Noise
| Demonstrate Technological Advancement | Low noise levels are often a reflection of high efficiency, precision design, and quality manufacturing, and are generally associated with greater energy efficiency and reliability. |
| Improved Work Environment | Significantly reduces noise pollution within the factory, meeting environmental requirements and benefiting employee health. |
| Application Scenarios | Low noise levels allow air compressors to be installed near noise-sensitive areas, such as offices, laboratories, or residential areas. |
3. Economic Benefits Beyond Noise Reduction
3.1 Productivity and Health Advantages
Although quiet air compressors can have a higher initial cost, the long-term benefits far outweigh the investment. Employees in quieter environments experience less fatigue, better communication, and reduced stress levels, which leads to measurable productivity improvements (5-15%). Additionally, quieter workplaces reduce the need for hearing protection, lowering operational costs and ensuring regulatory compliance.
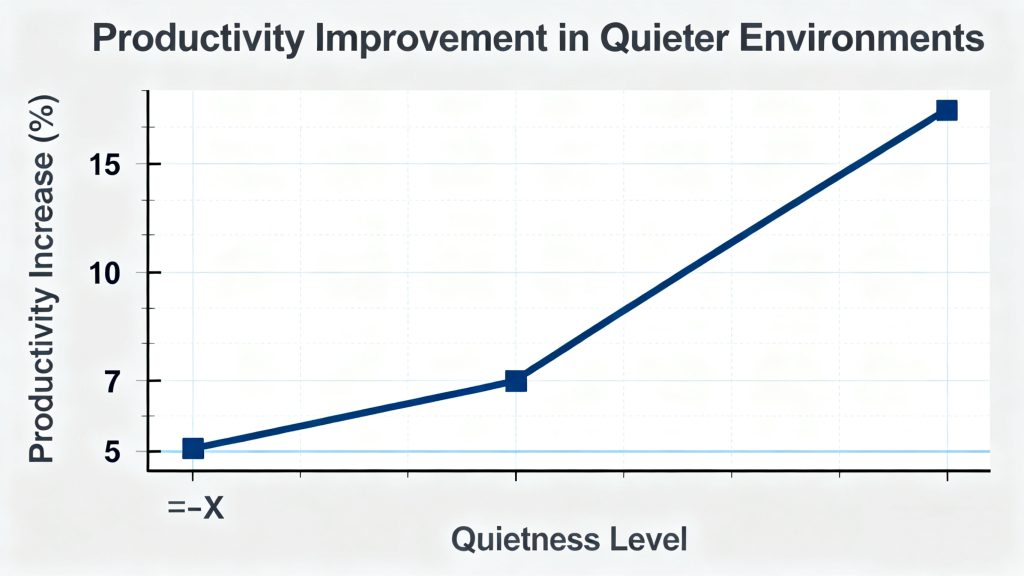
3.2 Energy Efficiency Correlations
The precision engineering of silent compressors also improves energy use. These models consume 20–30% less energy than conventional compressors. Quieter models often deliver the best efficiency because lower noise levels usually reflect smoother airflow and reduced mechanical loss.
Facilities that monitor both energy and noise often notice a clear pattern — lower dB means lower power bills. This makes quiet air compressors a smart investment for long-term operational savings.
Conclusion
The evolution of quiet air compressor technology has revolutionized industrial equipment design. Today’s silent compressors provide significant noise reduction without compromising performance. By improving worker wellbeing, reducing energy consumption, and meeting stringent noise regulations, quiet air compressors are transforming manufacturing environments. Manufacturers like Seize Air offer solutions that combine advanced noise-reduction technology with energy-efficient, oil-free screw compressors, demonstrating how system-level optimization can lead to greater performance and reliability.




 English
English
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português
 Deutsch
Deutsch






