An air compressor is indispensable power equipment in industrial production. It converts mechanical energy into gas pressure energy and provides a power source for all kinds of pneumatic tools, production lines, and equipment. With so many air compressors on the market, companies often have a hard time choosing between the traditional piston air compressor and the more advanced screw air compressor. How can the most suitable type of air compressor be matched to different industries and working conditions? This article introduces five types of air compressors commonly used in industry. It explains their working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and applicable scenarios. The article also provides advice for selecting the right air compressor.
Introduction: the importance of air compressors in industry
The air compressor is the “power heart” of modern industry and is widely used in manufacturing, energy, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and other fields. According to statistics, air compressors account for about 10-30% of total industrial electricity consumption, so choosing an efficient, reliable air compressor is crucial for reducing enterprises’ operating costs.
However, a wide range of air compressors are available on the market, from traditional piston types to advanced centrifugal types. Each type has its own unique operating principle and application. Many companies improperly select air compressors due to a lack of understanding of their performance characteristics. This can result in either overpowered equipment, which wastes energy, or underperforming equipment, which affects productivity.
This article will introduce the five most common types of air compressors in industry: piston, screw, centrifugal, sliding vane, and scroll. By comparing their technical parameters and application scenarios, we will help you choose the most suitable equipment for your needs.

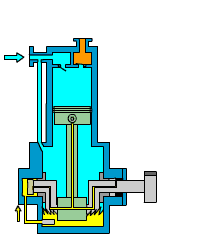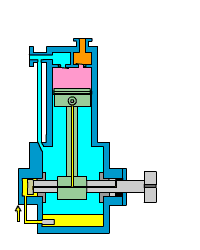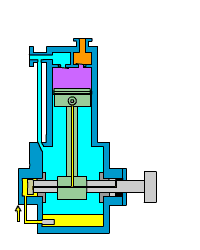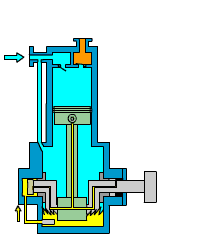
Piston (reciprocating) air compressor
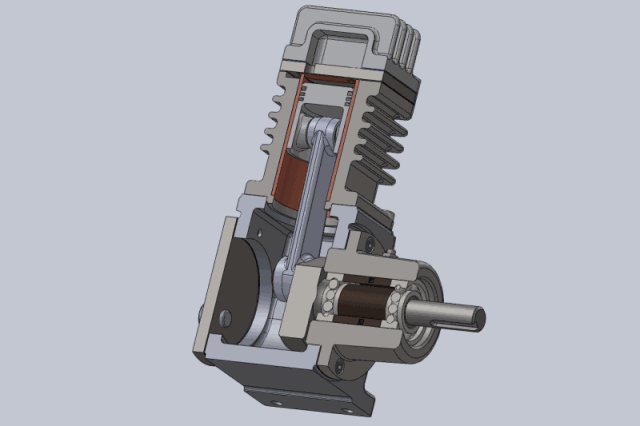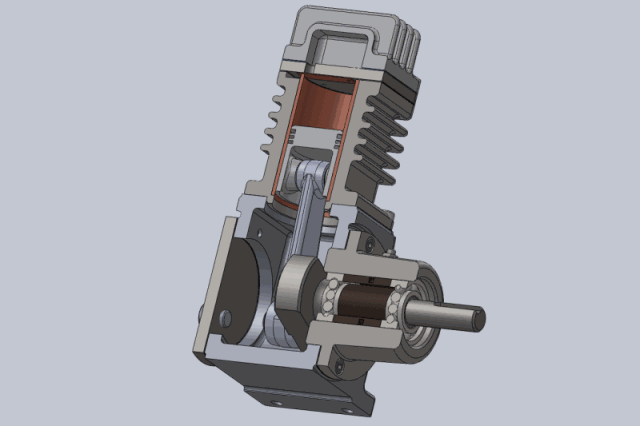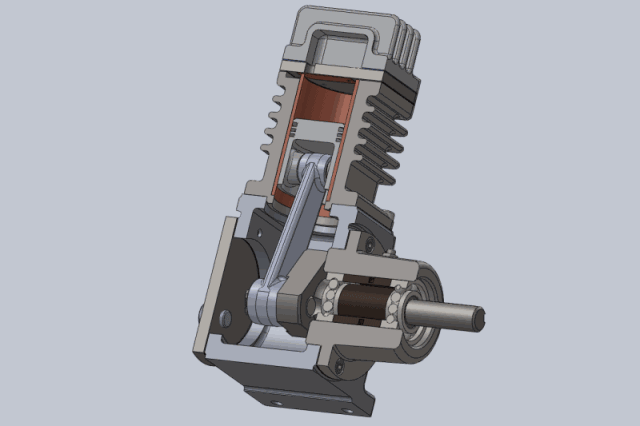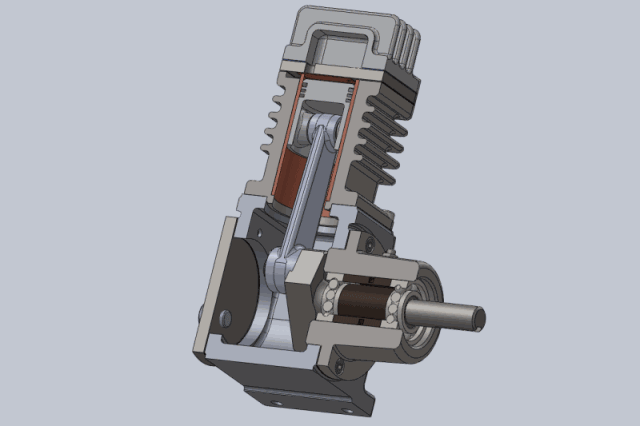
Piston air compressors are one of the oldest and most traditional types of compressors. They compress air using the reciprocating motion of a piston in a cylinder.
Working Principle:
A piston air compressor consists of a crankshaft, connecting rod, piston, cylinder, inlet valve, and exhaust valve. When operating, the crankshaft drives the piston to move back and forth in the cylinder.
- The suction process occurs when the piston moves downward, forming negative pressure in the cylinder. The inlet valve opens, and air is sucked into the cylinder.
- The compression process occurs when the piston moves upward and the cylinder volume decreases, compressing the air.
- The exhaust process occurs when the pressure reaches the set value. The exhaust valve opens, and the compressed air is discharged to the storage tank.
Piston compressors can be divided into oil-lubricated and oil-free according to their lubrication method.
Characteristics and parameters:
- Pressure range: 0.5-20 MPa. It is suitable for low-pressure to ultra-high-pressure scenarios.
- Flow rate range: 1-10 m³/min. It is suitable for small- to medium-sized air volume requirements.
- Energy efficiency: Medium
- Maintenance costs: Low for low-power systems; high for high-power systems.
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Advantages | ❌ Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ✔ Simple structure, low initial cost | ✖ High noise & vibration |
| ✔ Wide pressure range | ✖ Pulsating airflow (requires a buffer tank) |
| ✔ Suitable for intermittent use | ✖ High maintenance (wear-prone parts) |
Application Scenario:
The Piston Air Compressor is suitable for:
Piston air compressors are suitable for: Small workshops and vehicle repair stores that use pneumatic tools, such as nail guns and paint spray guns.
Occasions requiring high-pressure gas, such as high-pressure testing and gas cylinder filling.
Intermittent gas consumption scenarios
Screw Air Compressor
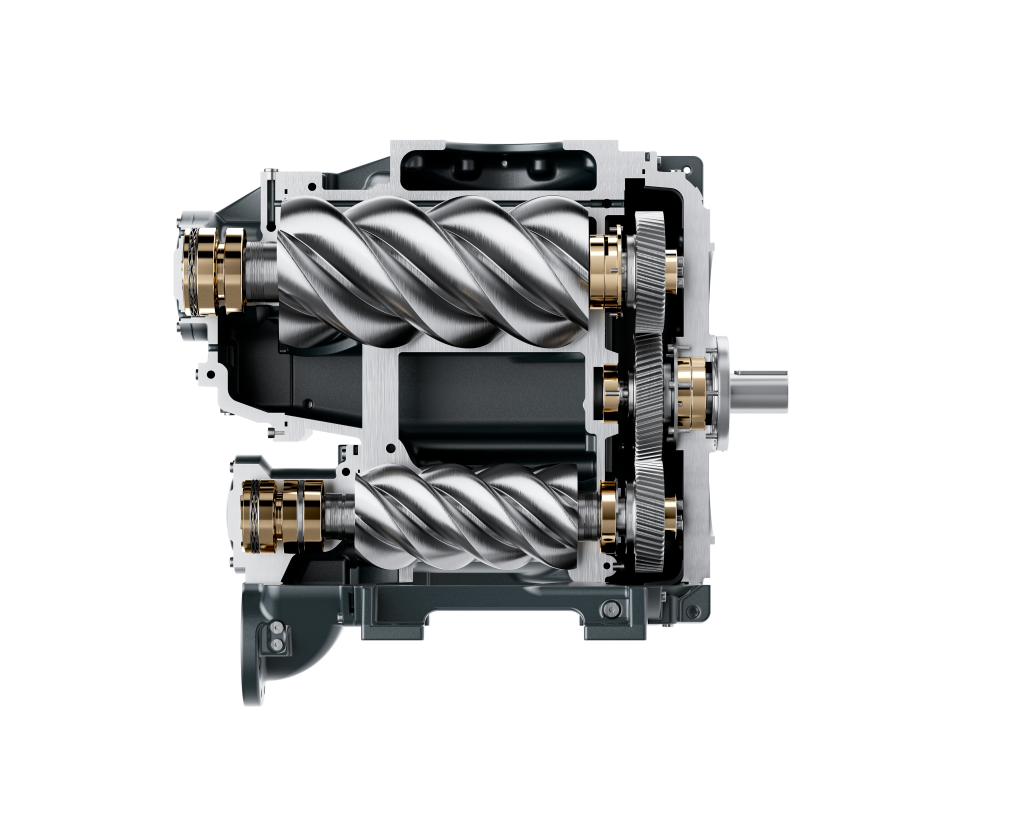

The screw air compressor is the most popular type of compressor in the industry today. It has a nearly 100% market share in the 1-60 m³/min flow range.
Working Principle:
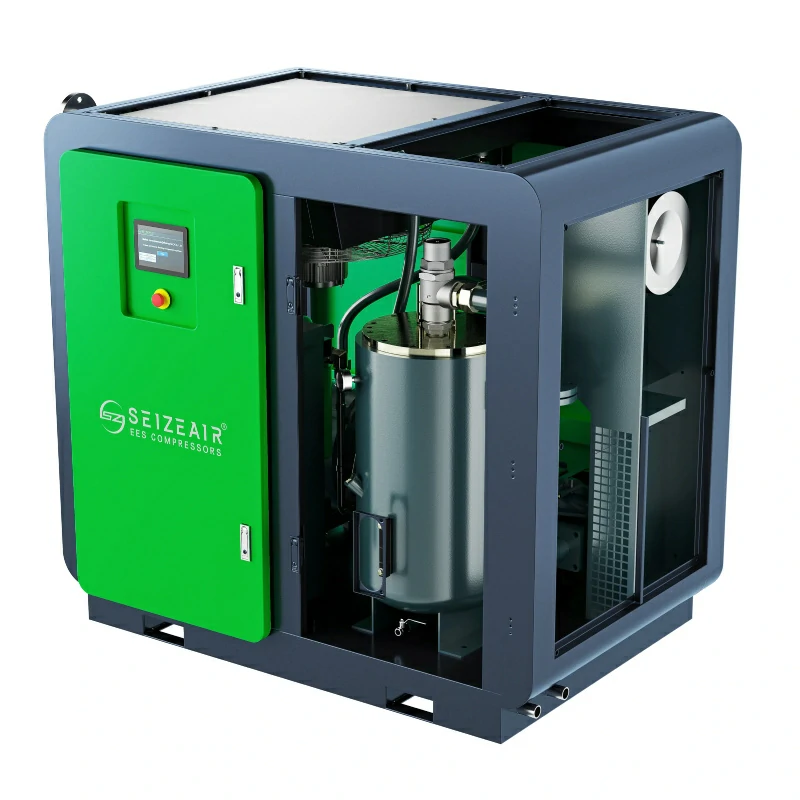
A screw air compressor compresses air through the rotary motion of a pair of mutually engaging rotors (screws).
Suction Process: Air enters the rotor engagement space through the air inlet.
Compression process: As the rotors rotate, the meshing space gradually decreases, compressing the air.
Exhaust process: The compressed air is discharged through the exhaust port.
A screw air compressor can be divided into two types:
1) According to the number of screws:
a. Single screw
b. Twin screw (99% of the market is twin screw)
2) According to the lubrication method: oil-injected and oil-free.
Characteristics and parameters:
- Pressure range: 0.5-1.0 MPa, suitable for medium-pressure applications
- Flow rate range: 1-60 m³/min. This meets the needs of most industries.
- Energy efficiency: High. The inverter screw machine can save 30%-40%.
- Maintenance cost is higher than that of a piston type, but it has fewer parts and a longer service life.
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Advantages | ❌ Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ✔ Smooth operation, low vibration | ✖ Higher initial cost |
| ✔ Continuous airflow (no pulsation) | ✖ Complex maintenance (requires skilled technicians) |
| ✔ Energy-efficient (VSD models available) | ✖ Performance drops if rotor wear occurs |
Application Scenario:
Screw air compressors are widely used in:
- Continuous production lines in the manufacturing industry (automobile, electronics, textiles, etc.).
- Chemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries that require high air quality
- Occasions that require 24-hour continuous operation
Centrifugal air compressors
A centrifugal air compressor is a high-flow, high-efficiency compressor designed for large industrial systems.
Working Principle:
The centrifugal air compressor works on air through an impeller that rotates at high speeds.
In the acceleration stage, air enters the impeller and gains speed due to centrifugal force.
In the compression stage, high-speed air flows through the diffuser, reducing its speed and converting its kinetic energy into pressure energy.
In the cooling stage, if there is multi-stage compression, a cooler reduces the air temperature.
A centrifugal air compressor usually consists of two to three impellers that rotate at speeds of 5,000 to 15,000 rpm.
Characteristics and parameters:
Pressure range: 0.4-1.3 MPa
Flow rate range: >100 m³/min
Suitable for large flow rate requirements
Energy efficiency: Extremely high; significant energy savings.
Maintenance cost: Low. Parts have a lifespan of up to 15 years.
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Advantages | ❌ Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ✔ High capacity (ideal for large plants) | ✖ Expensive initial investment |
| ✔ Oil-free operation (ISO Class 0) | ✖ Not suitable for small-scale use |
| ✔ Compact footprint | ✖ Susceptible to “surge” (requires anti-surge controls) |
Application scenario:
Centrifugal air compressors are mainly used in:
- Aerodynamic systems of large-scale chemical and iron and steel enterprises
- High-flow requirements in the power and air separation industries
- Occasions requiring extremely high compressed air quality (e.g., electronics and medicine)
Sliding vane compressors
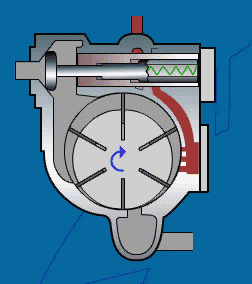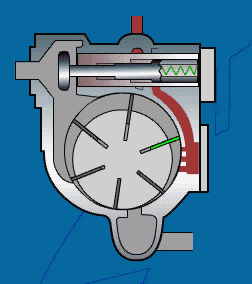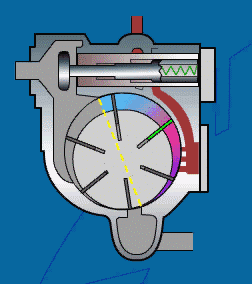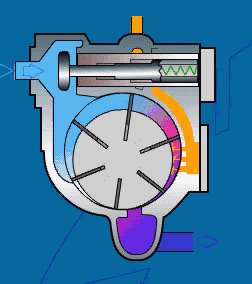
A sliding vane air compressor is a type of rotary compressor that has a simple structure and a compact size.
Working Principle:
A sliding vane air compressor consists of an eccentric rotor and a radial sliding vane.
The rotor is eccentrically mounted in the cylinder and has a radial sliding vane.
As the rotor rotates, the vane moves toward the inner wall of the cylinder due to centrifugal force.
The enclosed space formed by the vane and the cylinder continuously changes volume, thereby achieving air inhalation, compression, and discharge.
Characteristics and Parameters
Pressure range: 0.7-1.0 MPa
Flow rate range: 1-20 m³/min
Energy efficiency: low
Maintenance cost: Medium. Slide plate wears out faster.
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Advantages | ❌ Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ✔ Ultra-quiet (<60 dB) | ✖ Limited pressure & flow range |
| ✔ Compact & lightweight | ✖ Not for heavy-duty industrial use |
| ✔ Oil-free operation | ✖ Difficult to repair (sealed design) |
Application scenarios:
Sliding vane air compressors are suitable for:
- Portable air tools
- Air supply for small equipment
- Space-constrained applications
Scroll compressor
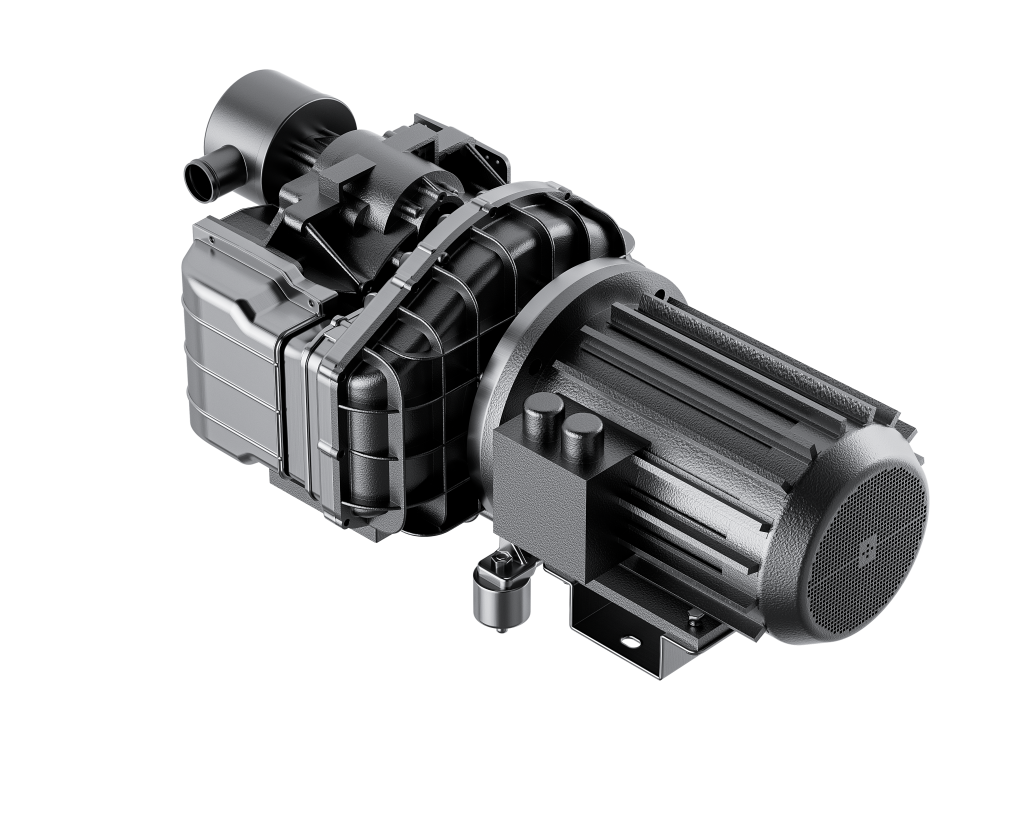

The scroll compressor is a new type of high-efficiency compressor used in specific fields due to its quiet and compact design.
Working Principle:
A scroll air compressor consists of a static scroll disk and a moving scroll disk.
The movable scroll disk moves eccentrically relative to the static scroll disk.
The two disks engage to form a series of crescent-shaped confined spaces.
As the moving scroll disk moves, the confined spaces move toward the center. This decreases the volume and compresses the air.
Characteristics and Parameters:
Pressure range: 0.3-0.8 MPa
Flow rate range: 0.5-10 m³/min
Energy efficiency: Medium
Maintenance cost: Low; no wearing parts.
Pros & Cons
| ✅ Advantages | ❌ Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ✔ Simple design, compact size | ✖ Lower efficiency (higher energy use) |
| ✔ Smooth airflow | ✖ Frequent vane replacements |
| ✔ Portable (used in mobile applications) | ✖ Not for high-pressure needs |
Application scenarios:
Scroll air compressors are mainly used in:
- Hospitals
- Laboratories
- Other noise-sensitive environments
- Air supply for small precision instruments
- High-end applications with space constraints

Air Compressor Selection Guide:
Selecting the right air compressor requires considering many factors.
The following are some key selection principles:
- Determine the working pressure.
The rated exhaust pressure of an air compressor should be about 20% higher than the maximum working pressure of the pneumatic system.
Consider pipeline pressure loss, which is usually 0.15–0.2 MPa.
Pressure unit conversion: 1 bar = 0.1 MPa ≈ 1 kg/cm².
- Calculate the air demand.
Add the flow rates of all air-using equipment together and increase the sum by 20%.
Flow rates are measured in m³/min (cubic meters per minute) or L/min (liters per minute).
For widely fluctuating air loads, consider the “high and low pressure split” option.
- Select a compressor type.
Small flow, high pressure: Piston type
Medium flow and continuous operation: Screw type (frequency conversion is more energy efficient).
Large flow with no oil requirement: centrifugal type
Portable, small-scale: Sliding vane type
Quiet and clean: scroll type
- Consider energy efficiency.
Inverter compressors can save 20%-40% of energy.
Permanent magnet motors are more efficient than standard motors.
Two-stage compression is 10%-15% more energy efficient than single-stage compression.
- Evaluate the total cost of ownership.
Consider not only the purchase cost, but also the long-term costs of energy consumption, maintenance, and replacement parts.
Although screw and centrifugal types require a high initial investment, their long-term operating costs may be lower.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Most Suitable Air Compressor
Selecting an air compressor requires more than a simple comparison of specifications. It is a systematic project that requires comprehensive consideration of technical parameters, usage scenarios, and economic benefits. Through this article, we hope you will understand this.
Each type of air compressor has its own unique advantages; there is no absolute “best,” only the “most suitable.”
When selecting a compressor, balance short-term investment with long-term benefits. Although high-efficiency equipment has a high initial cost, it can save energy costs in the long run.
Professional consulting is important. If you are unsure, seek advice from compressor manufacturers or professional engineers.
If you need help choosing a compressor or optimizing your existing system for energy efficiency, our team of experts is ready to assist you. Contact us today for a free, customized air compressor solution!




 English
English
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Português
Português
 Deutsch
Deutsch






